WP2a Proton Transmission Imaging
Anatomical and stopping power information required for target positioning and for accurate treatment planning will be acquired by proton radiographic and tomographic transmission imaging. As this allows to directly reconstruct proton stopping power relative to water (RSP), the use of protons for imaging can potentially lead to a superior range calculation accuracy compared to X-ray CT imaging. Our research activities are focused on the development of two proton imaging setups based on single-particle detection and integrating detectors.
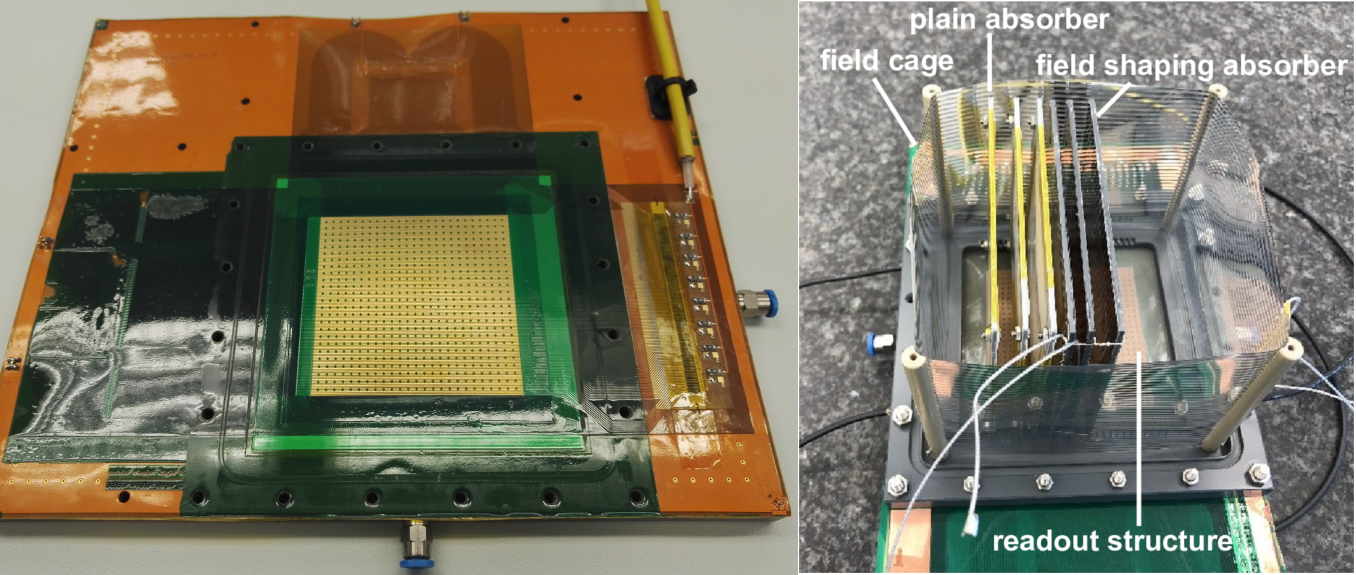
Figure 1: Readout structure of a prototype floating strip Micromegas tracker with two-dimensional strip readout (left) and prototype of a Time Projection Chamber with different vertical absorbers (right).
A dedicated system for proton CT (pCT) relying on single-particle tracking is developed and produced in-house. It consists of two low material budget Micromegas tracking detectors and a range telescope based on a time-projection-chamber (TPC) interleaved with multiple sub-mm thin Mylar absorbers (see Fig. 1). According to Monte Carlo simulations incorporating a detailed model of this detection system, an RSP accuracy better than 1% and a spatial resolution in the order of 2-3 mm-1 can be achieved. An example of a reconstructed pCT image of a water phantom with five tissue-equivalent material inserts is shown in Fig. 2.
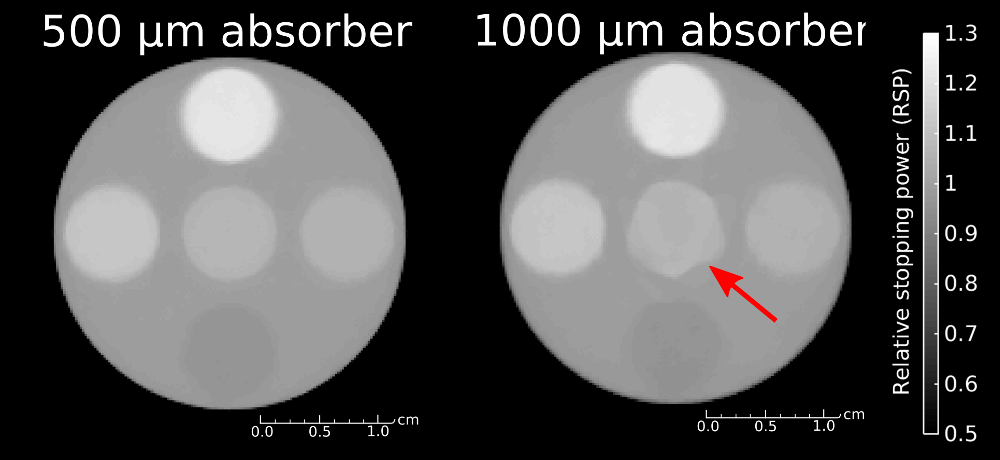

Figure 2: Reconstructed pCT slice of a water phantom with five different tissue equivalent inserts, simulated with Fluka for two different TPC absorber foil thicknesses.
The second approach based on integrating detectors is developed for usage at clinical facilities where the instantaneous beam current exceeds the detection capabilities of the single-particle tracking system (i.e., synchro-cyclotron based facilities). The object to be imaged is subsequently exposed to proton beams of multiple probing energies and the spatially resolved energy loss is measured using a large area CMOS sensor. Due to multiple Coulomb scattering inside the object, the expected spatial resolution is inferior to single-particle tracking, yet sub-mm spatial resolution is feasible according to Monte Carlo simulations.
Contact
Dr. Jona Bortfeldt
Dr. Matthias Würl
People
Dr. Jona Bortfeldt, Katrin Schürle, Dr. Matthias Würl, Prof. Dr. Katia Parodi
former members: Paulina Lämmer, Sebastian Meyer
References
Paper
Sebastian Meyer, Jonathan Bortfeldt, Paulina Lämmer, Franz Englbrecht, Marco Pinto, Katrin Schnürle, Matthias Würl, Katia Parodi; Optimization and performance study of a proton CT system for pre-clinical small animal imaging; Physics in Medicine & Biology; 2020; https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1361-6560/ab8afc
Conference contributions
Jona Bortfeldt, Sebastian Schinzel, Sebastian Meyer, Othmar Belker, Franz Englbrecht, Katrin Schnürle, Matthias Würl, Katia Parodi; Production and Test of an Aluminum Floating Strip Micromegas for Small Animal Proton Imaging; Talk given at the RD51 Mini-Week February 10 - 13 2020, CERN; 11.02.20
Jona Bortfeldt, Paulina Lämmer, Sebastian Meyer, Franz Englbrecht, John Gordon, Katrin Schnürle, Matthias Würl, Katia Parodi; Novel Micropattern Gaseous Detectors for a Small Animal Proton Irradiation Platform; Poster presented at the IEEE NSS/MIC conference 2019; 30.10.19
Sebastian Meyer, Jona Bortfeldt, Paulina Lämmer, Franz Englbrecht, Katrin Schnürle, Matthias Würl, Katia Parodi; Optimierung und Performance Evaluierung eines Protonen Computertomographie Systems für präklinische Bildgebung; Talk given at the 50th Annual Meeting of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Medizinische Physik; 20.10.
Jona Bortfeldt, Paulina Lämmer, Sebastian Meyer, Matthias Würl, Martin Hillbrand, Ralf Hertenberger, John Gordon, Katia Parodi; Entwicklung mikrostrukturierter Gasdetektoren für ein präklinisches Protonenbestrahlungssystem; Talk given at the 50th Annual Meeting of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Medizinische Physik; 18.09.19; https://epub.ub.uni-muenchen.de/70699/
Katrin Schnürle, Matthias Würl, Jannik Esslinger, Sebastian Meyer, Jona Bortfeldt, Franz Siegfried Englbrecht, Katia Parodi; Monte-Carlo-Studie zur Protonenradiographie für die Positionsverifikation für Kleintierbestrahlungen an einem klinischen Protonen-Therapiezentrum; Talk given at the 50th Annual Meeting of the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Medizinische Physik; 18.09.19; https://epub.ub.uni-muenchen.de/70700/
Jona Bortfeldt, Paulina Lämmer, Sebastian Meyer, Franz Englbrecht, Katrin Schnürle, Matthias Würl, Katia Parodi; Ultra-Thin Gaseous Detectors for for Small Animal Proton Transmission Imaging; Talk given at the International Workshop on Detection Systems and Techniques in Nuclear and Particle Physics; 12.09.19
Jona Bortfeldt, Paulina Lämmer, Sebastian Meyer, Franz Englbrecht, Katrin Schnürle, Matthias Würl, Katia Parodi; Development of Novel Ultra-Thin Micromegas and a Time Projection Chamber for Animal Ion Transmission Tomography; talk given at the 6th International Conference on Micro Pattern Gaseous Detectors; 08.05.19
Jona Bortfeldt, Paulina Lämmer, Sebastian Meyer, Franz Englbrecht, Katia Parodi; Development of a Time Projection Chamber for Ion Transmission Imaging; Poster presented at the Vienna Conference on Instrumentation; 20.02.19
Würl M, Moskal I, Carriço M, Meyer S, Englbrecht F, Pinto M, Schreiber J, Parodi K.; Feasibility study for small-animal proton radiography using passive energy variation and a single planar detector; 49. Jahrestagung der DGMP 2018, Nürnberg (Germany)
Meyer S, Bortfeldt J, Lämmer P, Englbrecht F, Schnürle K, Würl M, Parodi K; Optimization and performance evaluation of a proton computed tomography system for small animal imaging; 58th Annual Conference of the Particle Therapy Co-operative Group PTCOG58, Manchester (United Kingdom)

