Laser Ion Acceleration
Laser-driven ION (LION) acceleration can provide significant numbers of particles concentrated in bunches of very short duration and can enable hitherto inaccessible investigations of fast physical and chemical processes in matter. Recent progress in key pillars, including targetry, transport, instrumentation, and modeling has brought sincere applications within reach. Developing LION sources to a maturity that will enable first milestone demonstrations of novel discoveries in terra incognita represents our main motivation and promises long-term impact on applications of particle accelerators in science, technology, and medicine.
We are constantly looking for engaged students and welcome your applications. Please contact Joerg.Schreiber(at)lmu.de.
Find current lectures, exercises, and seminars at https://lsf.verwaltung.uni-muenchen.de/ and note that most master courses are also suitable for bachelor students.
-
The experimental station “laser-driven Ion (LION) Acceleration” serves research of this novel particle accelerator technology that is going to supplement the conventional ion sources crucial and is going to be used in physical basic research and in medicine as well.
more
-
Anything (even nothing) in the focus of the high power laser pulse can be considered as a target. It is developed and finessed within 'targetry'-activities. Those are the foundation of reliable conversion of laser-plasmas in applicable particle and photon radiation modalities, in particular for operating laser-driven ion acceleration.
more
-
Laser driven particle acceleration requires thorough understanding of electromagnetism, relativity, plasma physics and ultrafast phenomena. Advancing our knowledge is based on developing advanced experimental diagnostic methods in synergy with numerical simulations of relativistic laser plasma physics processes.
more
-
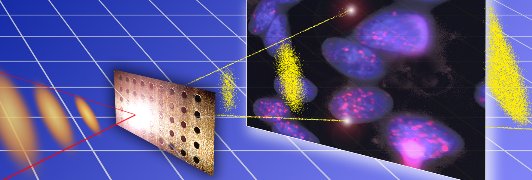
To match the compact size of the laser-driven ion source, we aim to miniaturize the systems for transporting and refocusing the bunches as well. One backbone solution is provided by inherently vacuum compatible permanent magnet quadrupoles. The challenge is to characterise the magnetic field distributions with high precision and develop positioning standards that enable positioning accuracy and repeatability in the micrometer range.
more
-
Development of detectors suitable for identification and characterization of laser accelerated ion bunches is of great importance, both for understanding the acceleration processes and subsequent applications. Our dedicated aim is to develop and implement online solutions for spatially and energy-resolved ion distribution measurements. Those must work reliably during the interaction of the high power laser pulse with the target. This poses a remarkable challenge, for example due to the tremendous electromagnetic pulse (EMP)
more
-
Monitoring our progress in source capability is essential for upcoming applications of laser-driven particle acceleration. Please visit our evolving website and please be invited to contribute
more