Penning traps
A Penning trap is a device to store charged particles such as ions of a defined charge-to-mass ratio q/m. Its working principle is based on the electromagnetic forces acting on charges. It consists of a superposition of an extremely homogeneous axial magnetic field B with an electrostatic quadrupole potential V0. The magnetic field causes a radial confinement towards its axis, while the resulting electric field is configured such that particles drifting along the z axis are reflected by a repulsive potential at the so-called endcap electrodes.
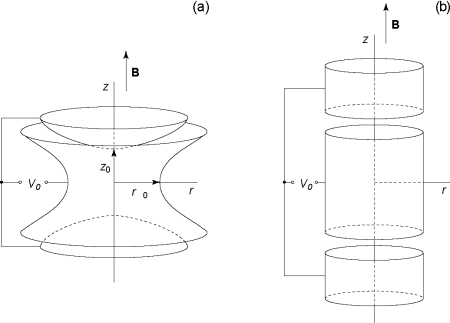
Typical configurations of trap electrodes: a) Hyperbolic and b) cylindrical trap, as implemented in MLLTRAP.

Photo of the MLLTRAP purification (left) and precision trap (right).
The resulting ion motion in these combined E and B fields is composed of three ideally harmonic oscillations with characteristic eigenfrequencies, an axial oscillation with the frequency wz and two radial motions, the modified cyclotron motion and the magnetron motion with the frequencies w+ and w-, respectively.
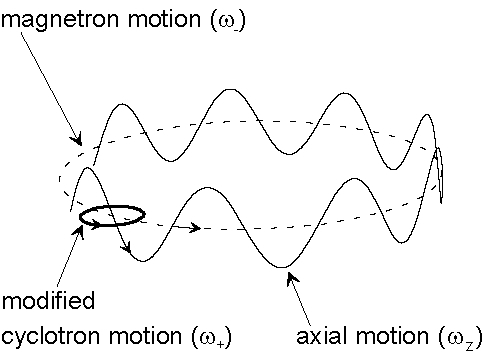
Characteristic ion motions in a Penning trap.

